Nutritional Content Analysis per Serving Size: Mountain Dew Nutrition Facts
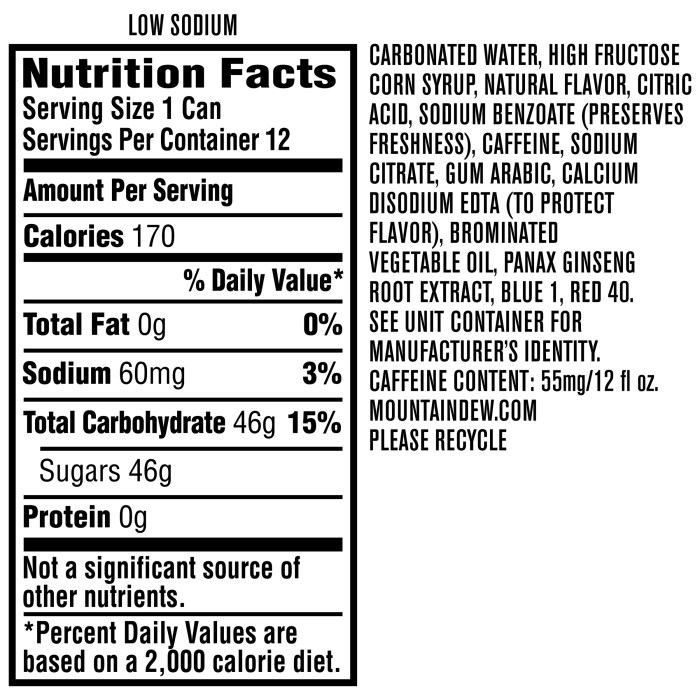
Mountain dew nutrition facts – Mountain Dew, a vibrant, citrus-flavored soda, boasts a bold taste that’s become iconic. However, understanding its nutritional profile is crucial for making informed choices about consumption. This section delves into the detailed nutritional content of a standard serving of Mountain Dew, compares it to other popular soft drinks, and explores the potential health implications of regular intake.
Mountain Dew Nutritional Information per Serving, Mountain dew nutrition facts
A standard 12-ounce serving of Mountain Dew contains a significant amount of sugar and calories, with minimal nutritional value. The following table presents a clear breakdown:
| Nutrient | Amount per 12 oz Serving |
|---|---|
| Calories | 170 |
| Total Carbohydrate | 46g |
| Sugars | 46g |
| Fat | 0g |
| Protein | 0g |
Note: Nutritional values can slightly vary depending on the specific Mountain Dew product and manufacturing variations. Always refer to the nutrition label on the specific product packaging for the most accurate information.
Comparison with Other Carbonated Soft Drinks
Compared to other popular carbonated soft drinks, Mountain Dew generally ranks higher in sugar and calorie content. For example, a 12-ounce serving of Coca-Cola typically contains around 140 calories and 39 grams of sugar, while a similar serving of Pepsi contains approximately 150 calories and 41 grams of sugar. Diet versions of these sodas will, of course, have significantly fewer calories and sugars.
The high sugar content in Mountain Dew is a key differentiator compared to these other options.
Potential Health Implications of Regular Mountain Dew Consumption
The high sugar and calorie content of Mountain Dew, coupled with its lack of essential nutrients, raises concerns about potential health implications associated with regular consumption. High sugar intake is linked to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and tooth decay. The absence of vitamins, minerals, and fiber means that Mountain Dew provides empty calories, contributing to overall poor nutrition.
Regular consumption can displace the intake of nutrient-rich foods, potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies. Individuals who regularly consume high amounts of sugary drinks like Mountain Dew often experience increased risk of various health problems. For example, studies have shown a correlation between high sugar intake and increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
Sugar Content and its Effects

Mountain Dew’s vibrant, citrusy flavor is undeniably appealing, but a significant contributor to this taste is its substantial sugar content. Understanding the type and quantity of sugars, and their subsequent impact on health, is crucial for making informed choices about consumption. This section will delve into the short-term and long-term effects of Mountain Dew’s high sugar load.
A 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew typically contains approximately 77 grams of sugar, primarily in the form of high-fructose corn syrup and sucrose. This translates to roughly 19.25 teaspoons of sugar – a significant portion of the recommended daily intake for most individuals. The high-fructose corn syrup is particularly concerning, as studies have linked its consumption to increased risks of various health problems.
Short-Term Effects of High Sugar Consumption
The immediate effects of consuming a large amount of sugar, such as that found in Mountain Dew, can include a rapid surge in blood sugar levels, leading to a subsequent energy crash. This rollercoaster effect can manifest as feelings of hyperactivity followed by fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Furthermore, the high sugar content can contribute to dental problems, as the sugar feeds bacteria in the mouth, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Imagine the sticky residue left on your teeth after a sugary drink; this provides a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
Long-Term Effects of High Sugar Consumption
Chronic high sugar consumption, such as that associated with regular Mountain Dew intake, is linked to a range of serious health consequences. Weight gain is a significant concern, as excess sugar contributes to an increased calorie intake without providing essential nutrients. This can lead to obesity, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
The consistent bombardment of teeth with sugar can also lead to severe tooth decay, requiring extensive dental work. For example, a person who drinks several cans of Mountain Dew daily might experience significantly accelerated tooth decay compared to someone who rarely consumes sugary drinks. The constant high blood sugar levels can also damage blood vessels and organs over time, further increasing the risk of long-term health problems.
Consider the case of individuals who develop type 2 diabetes due to long-term consumption of sugary beverages; this illustrates the severe long-term health consequences of such habits.
Comparison to Diet Mountain Dew
Mountain Dew and Diet Mountain Dew, while sharing a similar name and vibrant green hue, diverge significantly in their nutritional profiles. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed choices about beverage consumption. This comparison highlights the key distinctions in their ingredients and the potential impact on health.
Understanding the nutritional content of Mountain Dew, with its high sugar and caffeine levels, is crucial for managing your overall health. It’s important to consider the broader context of your dietary choices; for example, comparing the sugar content to something like a large Costco pizza, whose nutritional breakdown you can find here: costco pizza nutrition facts. Returning to Mountain Dew, mindful consumption is key to balancing enjoyment with well-being.
The primary difference lies in the sweetener. Regular Mountain Dew relies on high-fructose corn syrup and sucrose for its sweetness, contributing substantially to its calorie and sugar content. Diet Mountain Dew, conversely, uses artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose to achieve a similar taste without the added calories and sugars. This fundamental change ripples through the entire nutritional profile.
Nutritional Comparison
The following table provides a direct comparison of the nutritional information of a typical serving size (12 fl oz) of each beverage. Note that specific values may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and production batch.
| Nutrient | Mountain Dew | Diet Mountain Dew | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 170 | 0 | -170 |
| Total Fat (g) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sodium (mg) | 15 | 10 | -5 |
| Total Carbohydrate (g) | 46 | 0 | -46 |
| Sugars (g) | 46 | 0 | -46 |
| Protein (g) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Caffeine (mg) | 55 | 55 | 0 |
Ingredient Differences and Impact
The significant difference in sugar content directly impacts the calorie count. Regular Mountain Dew’s high sugar content contributes to a substantial calorie intake, which can contribute to weight gain if consumed regularly. The absence of sugar in Diet Mountain Dew results in zero calories. However, the use of artificial sweeteners raises other concerns. While not contributing to calorie intake, the long-term effects of artificial sweeteners on health are still under investigation and remain a subject of ongoing debate among scientists.
Potential Health Implications
Regular consumption of Mountain Dew, due to its high sugar content, can increase the risk of several health problems. These include weight gain, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and tooth decay. The high caffeine content can also lead to anxiety, insomnia, and digestive issues in some individuals. Diet Mountain Dew, while avoiding the sugar-related problems, still contains caffeine and artificial sweeteners, both of which have potential, though less understood, long-term health implications.
The impact of artificial sweeteners on gut health and overall metabolic function continues to be a subject of research.
Serving Size and Consumption Recommendations

Understanding serving size is crucial for managing your Mountain Dew intake and its impact on your overall health. A single serving, as defined on the nutrition label, provides a specific amount of sugar, caffeine, and other ingredients. Consuming multiple servings significantly amplifies these components, potentially leading to health consequences. The following information clarifies the relationship between serving size, nutritional intake, and responsible consumption.
The impact of different serving sizes on your daily nutritional intake is substantial. Consider the following examples based on a standard 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew, which is typically considered one serving. Consuming two cans doubles the sugar, caffeine, and calories ingested, significantly exceeding recommended daily limits for many individuals. Similarly, consuming three or more cans dramatically increases the potential negative health effects.
Serving Size and Nutritional Intake
The table below illustrates how varying Mountain Dew consumption affects your daily intake of key components. Note that individual needs and tolerances vary, and these figures represent averages based on a standard 12-ounce can.
| Serving Size (oz) | Calories | Sugar (grams) | Caffeine (mg) (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 (1 serving) | 170 | 46 | 55 |
| 24 (2 servings) | 340 | 92 | 110 |
| 36 (3 servings) | 510 | 138 | 165 |
| 48 (4 servings) | 680 | 184 | 220 |
Responsible Consumption Recommendations
Dietary guidelines generally recommend limiting added sugar intake. The high sugar content in Mountain Dew necessitates mindful consumption. Moderation is key; consider limiting yourself to one serving per day, or even less frequently. Substituting water or other healthier beverages is a beneficial strategy. Staying hydrated is crucial for overall well-being, and excessive sugary drinks can contribute to dehydration.
Consequences of Excessive Consumption
Excessive consumption of Mountain Dew, due to its high sugar and caffeine content, can lead to several adverse health effects. Regularly exceeding recommended serving sizes can contribute to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, dental problems, and even cardiovascular issues. The high caffeine content can lead to anxiety, insomnia, and digestive problems. Furthermore, the artificial colors and flavors found in many sodas are also subjects of ongoing research regarding potential long-term health implications.
For example, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition linked high sugar-sweetened beverage consumption to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions should exercise particular caution and consult with their healthcare providers before regular Mountain Dew consumption.
Quick FAQs
Is Mountain Dew suitable for children?
Due to its high sugar and caffeine content, Mountain Dew is not recommended for regular consumption by children. Moderation, if any, is advised.
Does Mountain Dew contain artificial colors?
Yes, Mountain Dew contains artificial colors. The specific colors may vary depending on the region and formulation.
What are the long-term effects of consuming Mountain Dew regularly?
Regular consumption of Mountain Dew can contribute to weight gain, dental problems, and other health issues due to its high sugar and caffeine content.
Are there healthier alternatives to Mountain Dew?
Yes, many healthier alternatives exist, including water, unsweetened tea, and naturally flavored sparkling water.
