Nutritional Composition of Mandarin Oranges
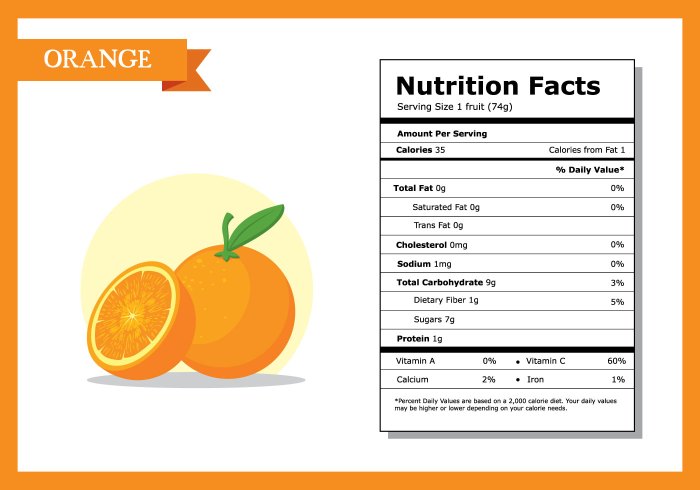
Nutrition facts on mandarin oranges – Mandarin oranges, a delightful citrus fruit, offer a refreshing taste and a surprising array of nutritional benefits. Their small size belies a significant contribution to a healthy diet, providing a concentrated source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This section details the macronutrient and micronutrient profile of mandarin oranges, highlighting their impact on overall well-being.
Macronutrient Composition of Mandarin Oranges, Nutrition facts on mandarin oranges
Mandarin oranges are primarily composed of carbohydrates, with a relatively low fat and protein content. A typical medium-sized mandarin orange (approximately 80 grams) contains approximately 15 grams of carbohydrates, of which a significant portion is natural sugars (fructose, glucose, and sucrose). This makes them a source of readily available energy. The fiber content contributes to digestive health, with around 1-2 grams per mandarin.
The fat content is negligible, typically less than 0.5 grams per serving, making them a suitable choice for those watching their fat intake. Protein content is also low, usually under 1 gram per serving. The balance of carbohydrates, fiber, and minimal fat and protein makes mandarin oranges a good choice for a balanced diet.
Vitamin and Mineral Content of Mandarin Oranges
Mandarin oranges are rich in several essential vitamins and minerals crucial for various bodily functions. They are an excellent source of Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant vital for immune function, collagen synthesis, and iron absorption. A medium-sized mandarin can provide around 30-40% of the recommended daily intake of Vitamin C. They also contain smaller amounts of other vitamins like Vitamin A (in the form of beta-carotene), thiamin (Vitamin B1), riboflavin (Vitamin B2), and folate (Vitamin B9), all essential for various metabolic processes.
In terms of minerals, mandarin oranges are a good source of potassium, an electrolyte crucial for maintaining fluid balance and blood pressure regulation. They also provide trace amounts of other minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. The combined presence of these vitamins and minerals contributes to overall health and well-being.
Antioxidant and Phytochemical Content of Mandarin Oranges
Mandarin oranges are packed with antioxidants and phytochemicals, contributing to their potential health benefits. These compounds combat oxidative stress, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
| Antioxidant/Phytochemical | Quantity (Approximate) | Role in Human Health | Potential Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 30-40mg per medium orange | Boosts immunity, collagen synthesis, antioxidant | Reduced risk of infections, improved skin health, protection against chronic diseases |
| Beta-carotene (provitamin A) | Variable, depends on variety and ripeness | Precursor to Vitamin A, antioxidant | Supports vision, immune function, skin health |
| Flavonoids (e.g., hesperidin) | Variable, depends on variety and ripeness | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | May reduce inflammation, improve cardiovascular health |
| Limonoids | Variable, depends on variety and ripeness | Antioxidant, anticancer properties | Potential role in cancer prevention |
Comparison with Other Citrus Fruits: Nutrition Facts On Mandarin Oranges

Mandarin oranges, while sharing the citrus family with oranges, grapefruits, and lemons, possess a unique nutritional profile and sensory experience. Comparing these fruits reveals interesting variations in their vitamin and mineral content, impacting their respective health benefits and culinary applications. Understanding these differences allows for informed choices based on individual nutritional needs and preferences.
A direct comparison highlights both similarities and key distinctions among these citrus fruits. While all are excellent sources of Vitamin C, variations in other nutrients and their overall flavor profiles create a diverse range of options for consumers.
Mandarin oranges offer a potent dose of Vitamin C and fiber, contributing to a healthy diet. For a balanced meal, consider pairing them with a side of rice, perhaps checking out the basmati rice nutrition facts to ensure a complete nutritional profile. Understanding both the mandarin orange and rice nutritional values helps in creating well-rounded, nutritious meals.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
The following table summarizes the key nutritional differences between mandarin oranges, oranges, grapefruits, and lemons. Note that values can vary depending on factors such as variety, growing conditions, and ripeness.
| Nutrient | Mandarin Orange (per 100g) | Orange (per 100g) | Grapefruit (per 100g) | Lemon (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (mg) | 40-50 | 50-60 | 40-50 | 50-60 |
| Fiber (g) | 1-2 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 |
| Potassium (mg) | 150-200 | 200-250 | 200-250 | 100-150 |
| Folate (mcg) | 15-20 | 15-20 | 10-15 | 5-10 |
This data illustrates that while all four fruits provide significant amounts of Vitamin C, oranges and grapefruits generally contain slightly higher levels compared to mandarins. Similarly, oranges and grapefruits tend to be richer in potassium and fiber. Lemons, while high in Vitamin C, are lower in other nutrients compared to the other three.
Sensory Characteristics and Health Implications
Beyond nutritional content, the sensory experience significantly differentiates these citrus fruits. These differences contribute to their diverse culinary applications and perceived health benefits.
- Taste: Mandarin oranges are known for their sweeter, less acidic taste compared to oranges, which have a more balanced sweet and tart profile. Grapefruits are distinctly tart and sometimes bitter, while lemons are intensely sour.
- Texture: Mandarins are easily peeled and segmented, offering a juicy, tender texture. Oranges are also juicy but require more effort to peel. Grapefruits have a firmer, less juicy texture, and lemons are generally less juicy with a thicker rind.
- Health Benefits: While all citrus fruits contribute to overall health through their vitamin and antioxidant content, some variations exist. For example, grapefruit’s interaction with certain medications is well-documented, requiring caution. The high fiber content in oranges and grapefruits promotes digestive health, while the concentrated Vitamin C in all these fruits supports immune function.
Mandarin Oranges in Culinary Applications

Mandarin oranges, with their vibrant flavor and convenient size, lend themselves beautifully to a wide range of culinary applications, extending far beyond simply eating them straight from the peel. Their versatility stems from their unique sensory profile and ease of preparation. Their delicate sweetness and refreshing acidity make them a welcome addition to both sweet and savory dishes.
The ease with which mandarin oranges can be incorporated into various recipes contributes to their popularity. Their segments are easily peeled and separated, requiring minimal preparation time. This convenience makes them an ideal ingredient for busy cooks seeking a quick and healthy addition to their meals.
Examples of Mandarin Orange Use in Recipes
The bright, zesty flavor of mandarin oranges complements a variety of dishes. Their delicate sweetness and refreshing acidity allow them to enhance both sweet and savory preparations.
- Salads: Mandarin orange segments add a burst of sweetness and color to salads, particularly those featuring greens, nuts, and cheeses. The contrast in textures and flavors creates a well-balanced and appealing dish. A simple combination of mixed greens, crumbled feta cheese, toasted almonds, and mandarin orange segments dressed with a light vinaigrette is both refreshing and nutritious.
- Desserts: Their sweetness makes them a natural fit for desserts. They can be added to cakes, muffins, and cookies, providing both moisture and flavor. Mandarin orange curd is a popular choice for tarts and fillings, showcasing the fruit’s bright citrus notes.
- Sauces and Glazes: Mandarin oranges can be pureed or juiced to create sauces and glazes for both sweet and savory dishes. A mandarin orange glaze adds a beautiful shine and tangy sweetness to roasted meats, particularly pork or duck. A reduction of mandarin orange juice with a touch of honey creates a delightful sauce for pancakes or waffles.
- Breakfast Dishes: Adding mandarin orange segments to oatmeal or yogurt provides a refreshing and nutritious start to the day. Their juice can also be incorporated into smoothies for a boost of vitamin C and flavor.
- Beverages: Mandarin orange juice is a refreshing beverage on its own or can be used as a base for cocktails or mocktails. It pairs well with other fruits, herbs, and spices, creating a variety of flavor combinations.
Preparing Mandarin Oranges for Consumption
Mandarin oranges require minimal preparation, contributing to their widespread appeal. Their ease of preparation makes them a convenient and healthy snack or ingredient.
- Eating Whole: Simply peel the mandarin orange and enjoy the segments. This is the quickest and easiest way to consume them.
- Juicing: Mandarin oranges can be juiced using a juicer or by hand. The juice is a refreshing beverage and can be used in cooking and baking.
- Adding to Salads: Peel the mandarin orange and separate the segments. Add the segments to salads just before serving to maintain their freshness and prevent them from releasing excess juice.
- Pureeing: Mandarin oranges can be pureed to create a smooth sauce or glaze. This is particularly useful in desserts or savory dishes.
Sensory Qualities of Mandarin Oranges
The sensory qualities of mandarin oranges—their taste, aroma, and texture—are key factors in their culinary appeal. These characteristics make them a desirable ingredient in a wide range of dishes.
Mandarin oranges possess a characteristically sweet and slightly tart taste, balanced by a subtle bitterness. Their aroma is intensely fragrant, with notes of citrus and floral undertones. The texture is juicy and slightly tender, offering a pleasant contrast to other ingredients in a dish. The combination of these sensory attributes makes mandarin oranges both appealing and versatile in culinary applications.
Popular Questions
Are mandarin oranges good for weight loss?
Mandarin oranges are relatively low in calories and high in fiber, which can contribute to feelings of fullness and aid in weight management. However, they should be part of a balanced diet and exercise plan for optimal weight loss results.
Can I eat mandarin oranges if I have acid reflux?
While generally well-tolerated, some individuals with acid reflux may find that citrus fruits, including mandarin oranges, can worsen their symptoms. It’s best to consume them in moderation and observe your body’s response.
Are mandarin oranges seasonal?
Yes, mandarin oranges have a specific growing season, typically from late fall to early spring. Availability may vary depending on your location.
How do I store mandarin oranges to keep them fresh?
Store mandarin oranges in the refrigerator to maintain their freshness for up to a week. Avoid storing them in direct sunlight or at room temperature for extended periods.
